From all sense, we have sense of sight, which is the most important. From the moment you came out in your mother’s womb to the very first time you see the face of your parents, our eyes are acting like a video camera that sends several of signals to our brain for processing.
Just take a moment and observe the things around you, would be believe that what you are actually seeing are the beams of light bouncing off the object and into your eyes? You may find it hard to believe, but it’s true. Our human eye is our only organ of vision that detects light. The simplest eyes can do nothing but detect the dark and light color of surroundings, while the more complex eyes can do more than that, it can even differentiate the shapes and colors of things around it.
The discovery of microscope is another pursuit of man to see things beyond the capabilities of our eyes, a remarkable device that enables the human eye by means of a lens or combination of lenses to observe enlarged images of tiny objects. It’s like seeing the world in different perspective.
Majority of microscopes are what we call and what is known as light microscopes since they rely entirely on light to observe the magnified image of an object.
It’s probably the most well known research tool in biology and other field of science.
And within this category, there are two main types of light microscopes, the compound or high power microscopes and the stereo microscopes or what known as the low power microscopes.
These two main categories have its specific capabilities and employs different magnification and illumination level.
Different Types of Microscope
1. Simple Microscope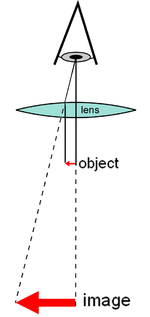
Simple microscope is the one which only uses a lens. The most classic example is a magnifying glass, therefore, it is the most basic microscope. The standard optical microscope uses a systems of two aligned lenses. The object to be observed is placed between the lens and the surface of the lens, which determines the formation of a virtual image; The greater the dipterous power of the lens and the farther away from the next point of view, the clearer the image will be of the object.
The Dutch Anthony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723), built a simple and very effective microscope based on a single lens. The microscope lacked aberrations that limited so much the effectiveness of the first compound microscopes, as the one used by Robert Hooke that produced an amplification of up to 300X, due to this, Leeuwenhoek was able to describe bacteria for the first time in history.
2. Compound Microscope
A microscope using more than one lens can be defined as a composite microscope to allow a sample to be viewed in an enlarged manner. The term is used in contrast to the concept of a simple microscope , in which only one lens is used and which is also known as a magnifying glass .
A compound microscope for instance is the most common type of microscopes, used basically for research and also referred to as biological microscope. It is called the high power microscope mainly because it’s magnification power can range up to 1000 times and some can even go up to 1500 times to 2000 times.
Parts of the compound microscope

Base
The part that comes to support the entire microscope.
Foot and support
It is the same base of the microscope, where it reaches to each of the parts of the compound microscope.
Column
It is also known as an arm or handle. It is located in the rear area of the device.
Ocular
It is the lens that is close to the eye of the observer, that is, the part of the microscope composed of where the observer looks at the sample. Through this, it is possible to increase the image of the objective. These usually have two eyepieces, called binoculars. However, there are models that only have one, which is named as monocular.
Arm
It is presented as a piece with a curved shape that can be easily rotated, which has the optical tube at its upper end and various pieces on the lower side.
Fine adjustment buttons
These are small buttons that are located on the two sides of the base of the arm, which help with the refinement of the focus.
Objective
It is the lens located near the preparation. This manages to increase the image of the sample to be observed.
Clamps
It refers to the mechanical part of the microscope with which the observer manages to hold the preparation to see. These are usually attached to a car with screws, in that modern equipment, with which the sample can be moved transversally or longitudinally.
Stir
It is in this part where the objective lens systems are found. Through it you can change and rotate the objectives. This usually contains eye lens systems.
Focus screws
It is a macro metric screw with which the approach can be approached, and at the same time, it is micrometric, used to obtain the correct focus.
Tube
The part that allows the observer to move the sample closer or closer, where it must move a micrometric screw that performs the rapid movement either up or down.
Lighting system
It is the part of the composite microscope that generates the light that impinges on the sample. Mobile car It is a device composed of two screws that are on top of the stage, which manages to move the sample to be observed creating an orthogonal movement from right to left, and from front to back.
Zipper
This part is what makes it possible for both micro and macrometric screws to be smaller or larger.
You can get some info about best pocket microscopes here.
3. Stereo Microscope

The stereoscopic microscope is a type of optical microscope that allows observing the sample generating an image in three dimensions. This is its main characteristic that distinguishes it from other microscopes where the sample is always observed in two dimensions.
While on the other hand, the stereo or dissecting microscope has a magnification power that range from 10 times to 80 times which is used for examining large specimens such as rocks and fossils, coins, stamps, hair follicles, plant and flower parts and other interesting objects.
Other types of microscope that we have today are the upgraded version of these two main types. These microscopes are usually comes with advanced technology and often times very expensive which is made specifically for medical and research purposes. So browse all those informative pages that we have and learn all types of microscopes and other related topics.
4. Optical Coherence Microscope

Optical coherence microscopy has the capability for use in the developmental biology in its capacity to image tissue areas that are unobtainable to standard microscopes. The high light dispersion characteristics of biological tissue make such methods as two-photon and confocal microscopy worthless for imaging a lot underneath the surface covering of tissue. Optical coherence microscopy prevails over this constraint letting three-dimensional imaging of cells or clusters of cells at depths of equal to one millimeter underneath the surface. The concept of the equipment facilitates imaging of biological samples safely and insidiously permitting the procedures to be observed in vivo. The method of the researchers to optical coherence microscopy offers a technique for creating three-dimensional time-lapse movies of tissue formation, an apparent benefit for developmental biologists with the help of contemporary visualization software.
5. Fluorescence Microscope
A fluorescence microscope is a light microscope used to study properties of organic or inorganic substances using the phenomena of fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, reflection and absorption.In most cases, a component of interest in the specimen is specifically labeled with a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore such as Green fluorescent protein, fluorescein or DyLight 488. The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength or wavelengths which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit longer wavelengths of light of a different color than the absorbed light. The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of an emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are the light source, Xenon or Mercury arc-discharge lamp, the excitation filter, the dichroic mirror or dichromatic beamsplitter, and the emission filter.
The filters and the dichroic are chosen to match the spectral excitation and emission characteristics of the fluorophore used to label the specimen. Most fluorescence microscopes in use are epi-fluorescence microscopes. These microscopes have become an important part in the field of biology, opening the doors for more advanced microscope designs, such as the confocal laser scanning microscope and the total internal reflection fluorescence microscope (TIRF). Fluorophores lose their ability to fluoresce as they are illuminated in a process called photobleaching. Special care must be taken to prevent photobleaching through the use of more robust fluorophores or by minimizing illumination.
6. Scanning Probe Microscope
In scanning probe microscopy or SPM, a physical probe is used either in close contact to the sample or nearly touching it. By rastering the probe across the sample, and by measuring the interactions between the sharp tip of the probe and the sample, a micrograph is generated. The exact nature of the interactions between the probe and the sample determines exactly what kind of SPM is being used. Because this kind of microscopy relies on the interactions between the tip and the sample, it generally only measures information about the surface of the sample.
Some kinds of SPMs are:
• Atomic force microscope
• Scanning tunneling microscope
• Electric force microscope
• Magnetic force microscope (MFM)
• Near-field scanning optical microscope
7. Point Projection Microscopes
The field emission microscope, field ion microscope, and the Atom Probe are examples of point-projection microscopes where ions are excited from a needle-shaped specimen and hit a detector. The Atom-Probe Tomograph (APT) is the most modern incarnation and allows a three-dimensional atom-by-atom (with chemical elements identified) reconstruction with sub-nanometer resolution.
8. Acoustic Microscopes
Acoustic microscopes use sound waves to measure variations in acoustic impedance. Similar to SONAR in principle, they are used for such jobs as detecting defects in the subsurfaces of materials including those found in integrated circuits.
10 Best Students Microscope Brands Reviews
1. Nikon
Nikon is a Japanese brand founded in 1917. It is especially known for building some of the best cameras in the world. Since the beginning of the company Nikon has also been dedicated to making microscopes.
Today Nikon is considered one of the best manufacturers of microscopes in terms of quality. Nikon builds high quality microscopes for both the field of biology and industrial applications. In its catalog you can find a wide variety of models ranging from binocular composite microscopes to stereoscopic microscopes or inverted microscopes.
Nikon Eclipse E200 Microscope
Nikon microscopes are designed to satisfy users in professional fields with very demanding requirements. Its products are authentic cutting-edge technology . This means that its price range is generally out of the reach of an amateur user. For beginners or amateurs of microscopy, the price of these microscopes may be excessive. Even so, it is always possible to get lucky in the second-hand market.
Among the Nikon microscopes that have marked an era among users of microscopes are the Nikon Eclipse E100 and the Nikon Eclipse E200 . These microscopes were designed to be used in laboratories and for educational purposes.
2. Zeiss
Zeiss is one of the emblematic brands in the history of microscopes. The company was founded by Carl Zeiss in 1846 and was responsible during the nineteenth century for major innovations in the construction of microscopes. Thanks to Ernst Abbe’s theory of optics and Otto Schott’s manufacture of high-quality lenses, Carl Zeiss managed to make a qualitative leap in the quality of microscopes.
Zeiss Primo Star microscope
Zeiss Primo Star (Source: Zeiss Microscopy )
After the death of its founder and until today, Zeiss has remained one of the leading manufacturers of microscopes. Besides dedicating itself to the manufacture of microscopes, Zeiss is one of the largest manufacturers of optical equipment in the world.
Zeiss stands out and is recognized for its capacity for innovation . Zeiss manufactures all kinds of microscopes, including electron microscopes. Your surgical microscopes are recognized in their field as the best that exist.
One of the best-known Zeiss microscopes is the Primo Star . This microscope has been designed to be used in an educational environment and stands out for its versatility and ease of use. As in the case of Nikon and as it happens with the big brands, these microscopes of such high quality can be out of reach of a beginner user with a limited budget.
3. Leica
Leica is the other flagship microscope manufacturer of German origin . The company was founded by Ernst Leitz in 1864. It is well known for its line of cameras and for manufacturing the optical lenses of many SLR cameras . Thanks to his knowledge in the manufacture of lenses, it is not surprising that he is also a great manufacturer of microscopes.
Leica DM300 microscope
Leica is known for its innovative spirit . At the beginning of the 20th century, it was the first manufacturer to introduce a fully functional binocular microscope . In recent years he has led, together with the University of Columbia, the development of SCAPE technology, a type of 3D microscopy that allows the observation of living organisms in real time.
In the Leica catalog you can find basic microscope models , confocal, stereoscopic, digital microscopes and for industrial and medical applications . Leica products stand out for their high quality and ergonomics . His stereoscopic microscopes are especially known in the educational field, among them the Leica EZ4 microscope stands out . Among its optical microscopes for students and fans of microscopy one of the most popular is the Leica DM300 .
4. Olympus
Olympus is, together with Nikon, one of the best-known Japanese microscope manufacturers. It has gained part of its good reputation thanks to the quality of its cameras . Olympus does not have the antiquity of other manufacturers such as Zeiss or Leica. It was founded in 1919 by Takeshi Yamashita . Even so it has demonstrated during the last century that it plays in the first league of manufacturers in the field of microscopy.
Olympus was one of the first manufacturers to dispute the European hegemony of the microscope market. The company has always distinguished itself by trying to develop instruments that are easy to use . For this reason Olympus microscopes stand out especially for their ergonomics and configuration versatility .
The Olympus models follow different lines to cover the different needs of the users. Among all series of microscopes, the BX , CX and SZ series stand out for stereoscopic microscopes.
5. Meiji Techno
Meiji Techno is perhaps not as well known as the previous brands. Even so, it is the third largest Japanese microscope manufacturer behind only Nikon and Olympus. Meiji is a particularly strong manufacturer in the field of microscopes for educational and industrial fields .The fact that Meiji Techno is not as well known as the other brands makes the price-quality ratio of its products more advantageous. Meiji Techno is undoubtedly a rising value in the field of microscopy increasingly valued by users. In recent years Meiji Techno has begun to expand into other sectors of microscopy with advanced models of microscopes. Even so, their models for students continue to be the most popular.
6. Motic
Motic BA210 microscope
Motic is the best known brand of microscopes founded and established in China . The company is located in Hong Kong specifically and is less than 30 years old. The models of microscopes that it sells are aimed at superior students and applications for researchers . His specialization is in compound and stereoscopic microscopes as well as in digital microscopes and digital cameras for microscopes.
The quality of its microscopes has been increasing as the company has gained experience and maturity. If we consider that Nikon, Leica, Zeiss and Olympus are the upper class in the world of microscopes, it could be said that Motic is the middle class . Their prices are especially competitive compared to the brands mentioned above.
Among its models of stereoscopic microscope stand out for its low price those of the SFC-11 series . Motic also has in its catalog many models oriented to students and educational environments. Among them, the BA210 is particularly popular and can be found in binocular or trinocular versions.
7. Bresser
Bresser Biolux NV Microscope
Bresser is a German company founded in 1957 by Josef Bresser . Initially the company was dedicated exclusively to the manufacture of binoculars. Little by little it was expanding its offer also building other optical instruments such as telescopes or microscopes.
Currently the main supplier of Bresser is the Chinese manufacturer Jinghua Optical & Electronics . The instruments built by Bresser are marketed under the name of Bresser and also as National Geographic . Bresser is especially known for its series of microscopes ” Bresser Junior ” aimed at young students and beginners of microscopy.
Even so, it also offers professional material for laboratories, such as trinocular microscopes and inverted microscopes.
8. AmScope
AmScope is an American microscope manufacturer founded in 1996. The goal of AmScope is to offer microscopes for all types of applications at the lowest possible price . Currently offers more than 500 models to meet the different needs of users, whether students with little experience as research professionals.
One of the strengths of AmScope’s microscopes is that they also offer a wide variety of accessories for the microscope. This allows you to buy microscopes with very basic configurations that can be expanded with the purchase of accessories as needed.
AmScope has in its catalog many microscopes aimed at students who are beginning in the world of microscopy. Many of these come with starter packs that contain sample preparations and the necessary tools to use the microscope.
9. Celestron
Celestron is a company well known for being one of the most important telescope manufacturers . Its headquarters is located in California and was founded in 1964.
Celestron is also dedicated to the manufacture of other optical instruments , including cameras, binoculars and microscopes. One of the main advantages of Celestron microscopes is their low price . Celestron does not offer microscopes for professional equipment, its microscopes are simple and designed to meet the needs of beginner users and young students. In its catalog we can find monocular, binocular, digital and stereoscopic microscopes.
Among your Celestron microscopes, your USB microscopes are very popular . These microscopes transmit a digital image to the computer and are very useful for assembling circuits, watchmaking, etc.
10. Euromex
Euromex MicroBlue Microscope
Euromex is a manufacturer of microscopes founded in 1966 and located in Arnhem , in the Netherlands. Despite being a relatively new company compared to other European manufacturers, Euromex offers a wide range of microscopes.
For educational environments and young students, its MicroBlue monocular microscope and its EduBlue stereomicroscope are especially popular . Euromex also produces more advanced microscopes for industrial applications and research.

Comment:also include the uses